Health & Wellbeing
Our experts show you simple and effective ways to stay healthy and active, so you can live your passions every day.

Do you know your risk of glaucoma?
Glaucoma can result in blindness but rarely causes symptoms in the early stages. Discover if you’re at risk and how you can protect your eyes.
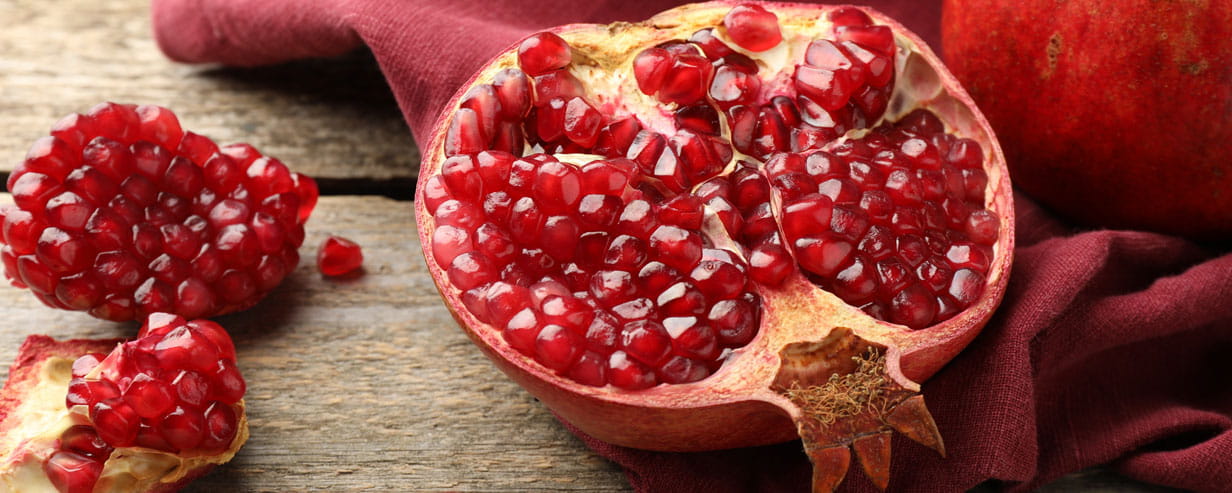

Are pomegranates the new superfood for older people?
The 6 surprising health benefits of pomegranates as we age.
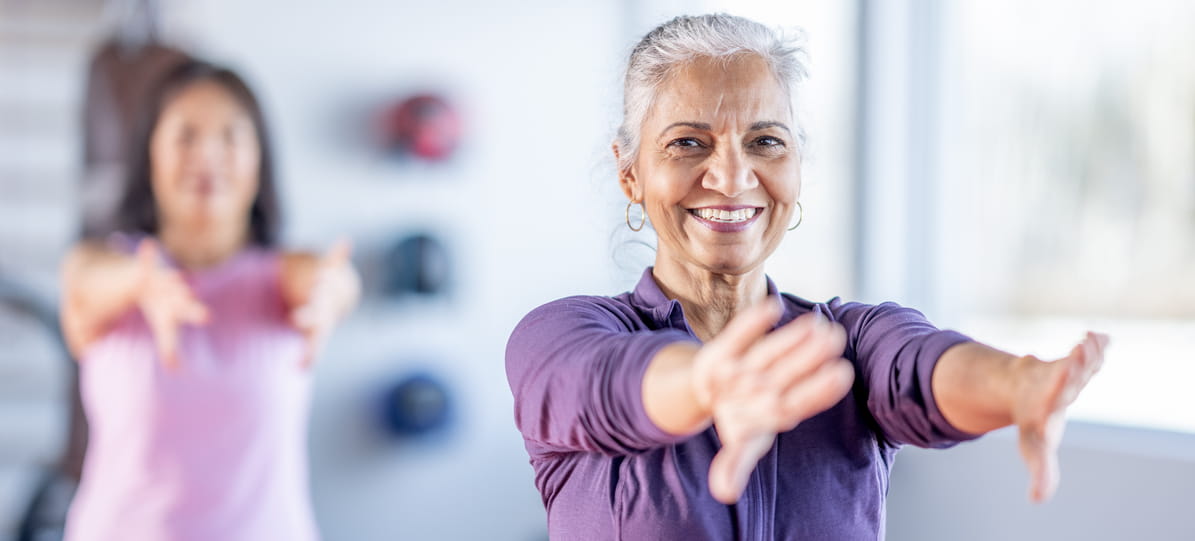

The secret to longevity: the science behind a long life
New studies reveal that you don’t build longevity through dramatic life overhauls, but through tiny daily changes that all add up.
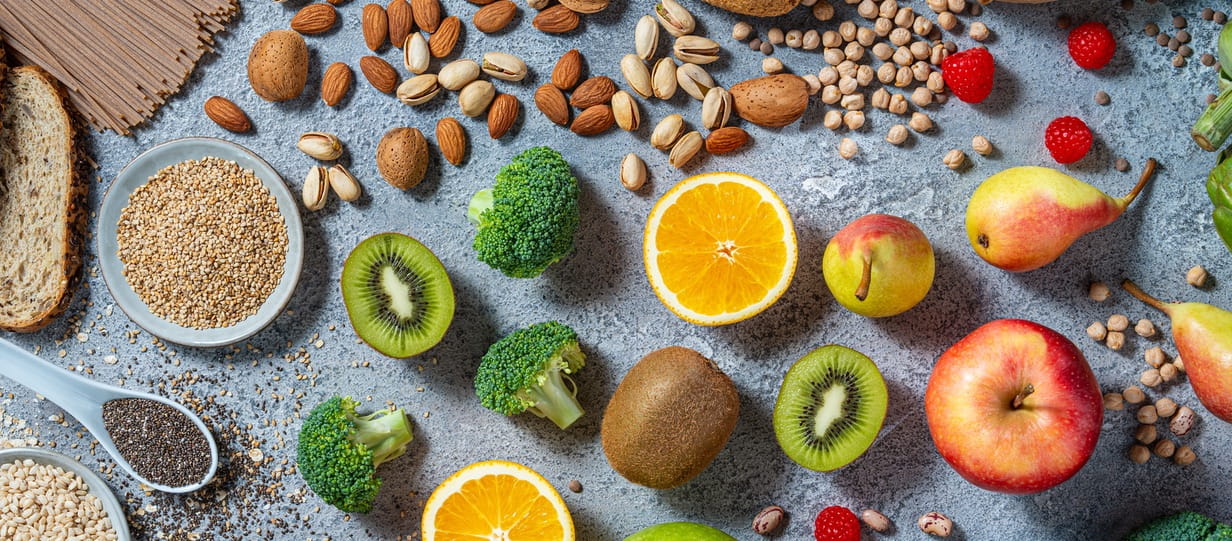

Easy ways to eat more fibre
It’s surprisingly easy to up the amount of fibre in your diet with just some small changes.
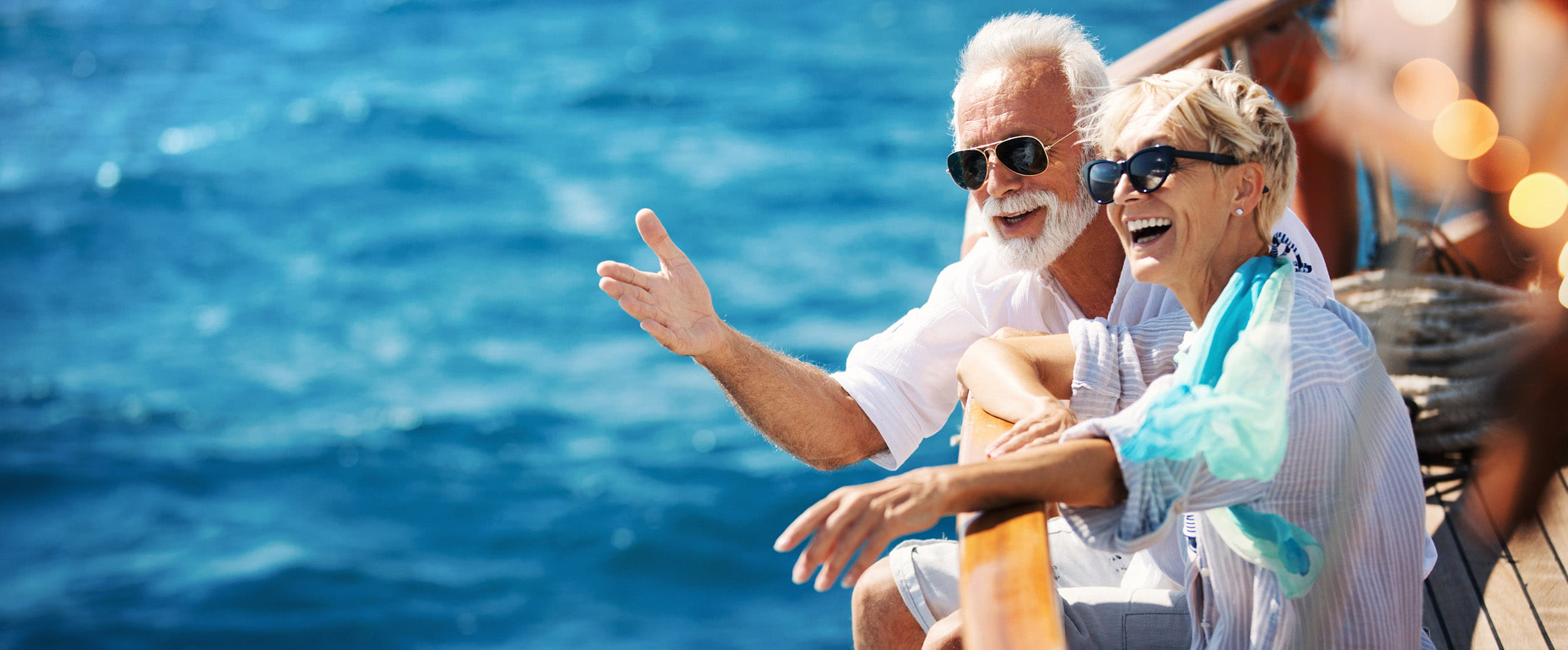

What’s the best age to retire? The pros and cons of retiring in your 50s, 60s and 70s
Are you retiring at the wrong age? The best age to retire for your body, brain, happiness and pocket.
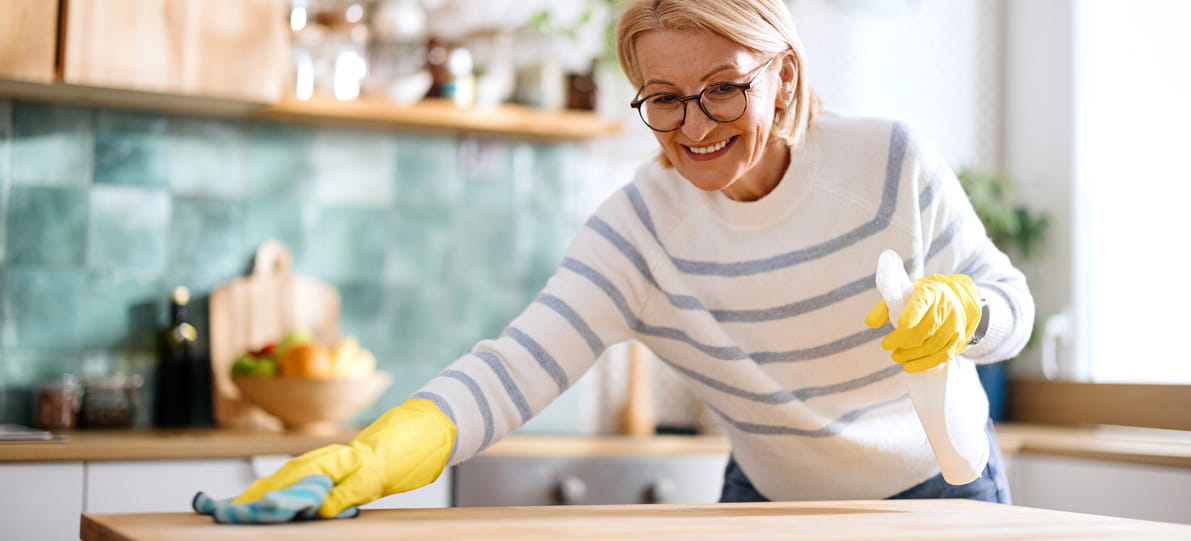

Is being too clean bad for your health?
We scrub, spray and sanitise our homes, but experts now say that dirt isn’t always the enemy.
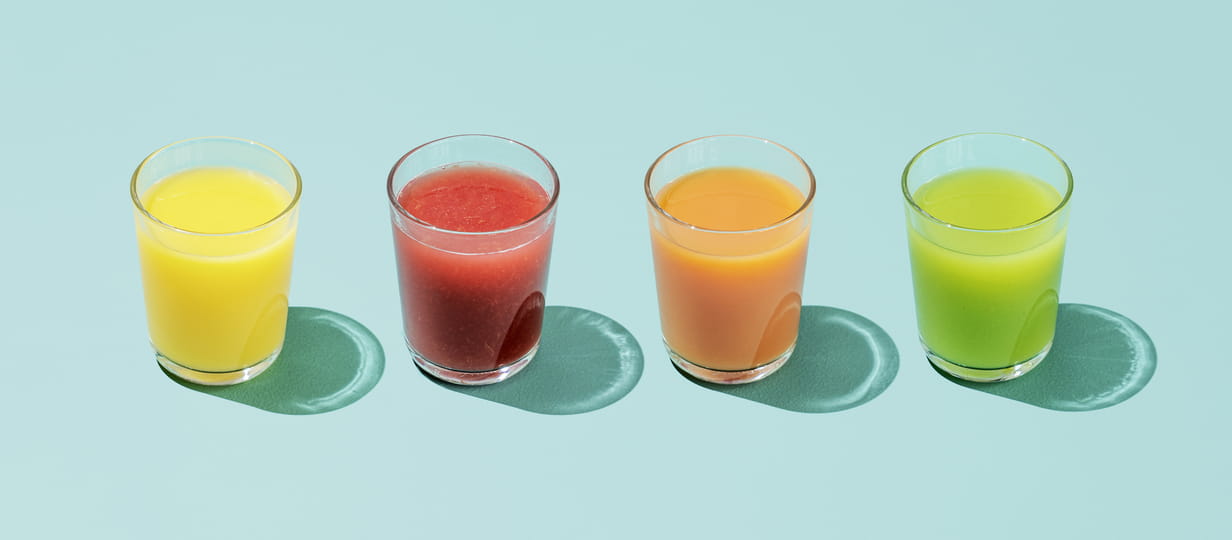

Could your morning fruit juice be raising your cancer risk?
Our nutrition experts share the best and worst juices for your health – and they might surprise you.
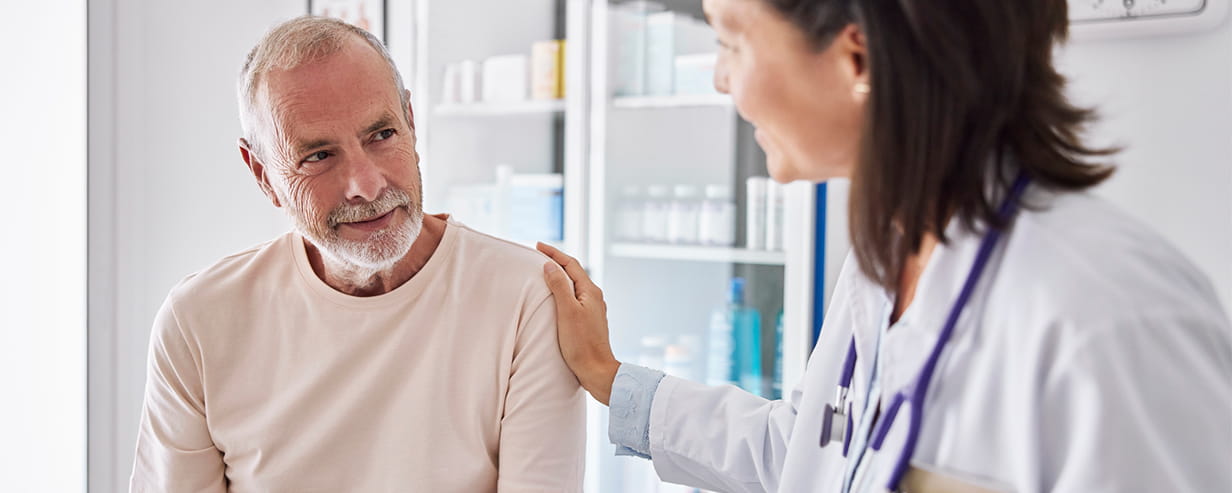
Enlarged prostate: the best new treatments
There’s now a raft of minimally invasive options for men suffering from the troublesome symptoms of an enlarged prostate (BPH). We look at the latest.

Is being too clean bad for your health?
We scrub, spray and sanitise our homes, but experts now say that dirt isn’t always the enemy.

Do you know your risk of glaucoma?
Glaucoma can result in blindness but rarely causes symptoms in the early stages. Discover if you’re at risk and how you can protect your eyes.

Easy ways to eat more fibre
It’s surprisingly easy to up the amount of fibre in your diet with just some small changes.
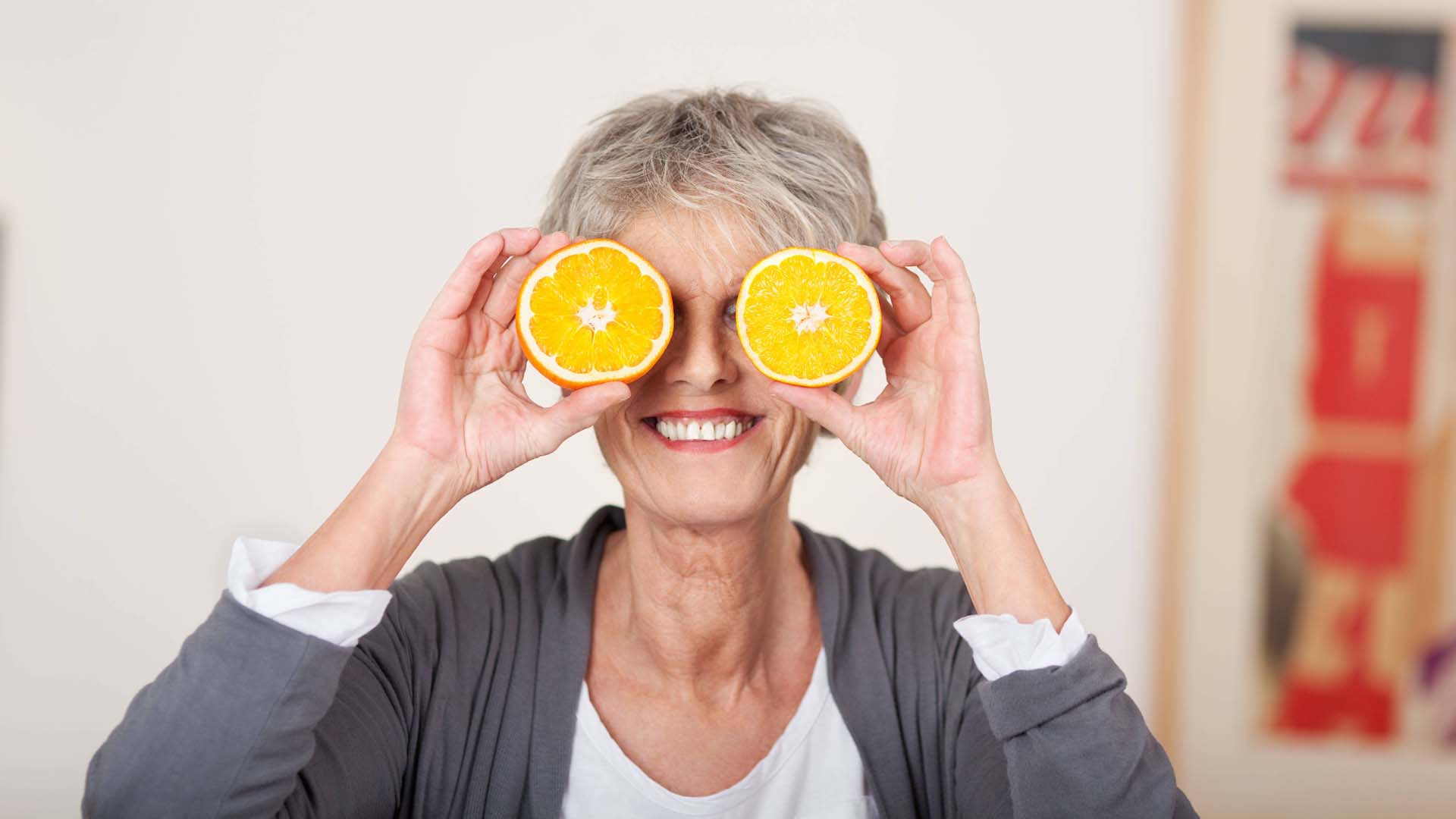

7 best foods for eye health – are you eating them?
A dietician reveals which foods can help protect vision and prevent age-related eye conditions.

Foods that may shorten your lifespan
Here’s what the experts say, plus simple swaps to help you stay stronger and healthier.

Dr Mark Porter on how to treat Achilles tendonitis
The best way to treat a sore Achilles tendon, by our medical expert.

For a limited time, enjoy 3 issues of Saga Magazine for just £1. Receive the next 3 print editions delivered direct to your door, plus 3 months’ unlimited access to the Saga Magazine app—perfect for reading on the go.
Don’t miss your chance to experience award-winning content at an exceptional price.
Play our free daily puzzles
Beat the boredom and exercise your mind with our selection of free puzzles.





